Task 4.1
Consider the curve $\vec r(t) = (2t+3, 4(2t-1)^2)$.
- Construct a graph of $\vec r$ for $0\leq t\leq 2$.
- If this curve represents the path of a rover (meters for distance, minutes for time), find the velocity of the rover at any time $t$, and then specifically at $t=1$. What is the rover's speed at $t=1$?
- Give a vector equation of the tangent line to $\vec r$ at $t=1$. Include this on your graph.
- State the rover's acceleration vector.
- Explain how to obtain the slope of the tangent line, and then write an equation of the tangent line using point-slope form. [Hint: How can you turn the direction vector, which involves $(dx/dt)$ and $(dy/dt)$, into the number given by the slope $(dy/dx)$?]
Task 4.2
We are ready to tackle the problem of finding the length of a path. This length we call arc length. If a rover moves at a constant speed, then the distance traveled is simply $$\text{distance} = \text{speed}\times\text{time}.$$ This requires that the speed be constant. What if the speed is not constant? Over a really small time interval $dt$, the speed is almost constant, so we can still use the idea above.
Suppose a rover (or other object) moves along the path given by $\vec r(t)=(x(t),y(t))$ for $a\leq t\leq b$. We know that the velocity is $\dfrac{d\vec r}{dt}$, and so the speed is just the magnitude of this vector.
- Show that we can write the rover's speed at any time $t$ as $$\ds\sqrt{\left(\frac{dx}{dt}\right)^2+\left(\frac{dy}{dt}\right)^2}.$$
- If the rover moves at speed $\ds\sqrt{\left(\frac{dx}{dt}\right)^2+\left(\frac{dy}{dt}\right)^2}$ for a little time length $dt$, what's the little distance $ds$ that the rover traveled?
- Explain (Riemann sums may help) why the length of the path given by $\vec r(t)$ for $a\leq t\leq b$ is $$s=\int ds=\int_a^b \left|\frac{d\vec r}{dt}\right| dt=\int_a^b \sqrt{\left(\frac{dx}{dt}\right)^2+\left(\frac{dy}{dt}\right)^2}dt.$$
- The path $\vec r(t) = (3\cos t, 3\sin t)$ for $0\leq t\leq 2\pi$ is a circle of radius 3. Verify that the formula above does in fact yield the circumference of this circle.
- If the curve is in space (so $\vec r(t)=(x(t),y(t),z(t))$ is the path), then how does the arc length formula above change?
- Are there any requirements we must know about the parametrization $\vec r$ so that the formula above is valid?
Task 4.3
Gravity is often the first example we encounter of a vector field. Other important vector fields arise when we study magnetism, electricity, fluid flow, and more. To analyze how a river flows, we can construct a plot of the river and at each point in the river we draw a vector that represents the velocity at that point. This creates a collection of many vectors drawn all at once, where the base of each velocity vector is placed at the point where the velocity occurs. For gravity, a similar picture can be drawn, though all the vectors will point down with the same magnitude. This task has us construct a plot of a vector field.
Consider the function $\vec F(x,y) = \left<x-2y,x+y\right>$. This is a function where the input is a point $(x,y)$ in the plane, and the output is the vector $\left<x-2y,x+y\right>$. For example, if we input the point $(1,0)$, then the output is $\left<1-2(0),1+0\right> = \left<1,1\right>$. To construct a vector field plot, we draw the vector $\left<1,1\right>$ with its base located at the input $(1,0)$. In the picture below, based at $(1,0)$ we draw a vector that points right 1 and up 1.
- Complete the table below and add the other 7 vectors to the graph.
\(\begin{array}{c|c} (x,y)&\left<x-2y,x+y\right>\\\hline (1,0)&\left<1,1\right>\\ (1,1)&\\ (1,-1)&\\ (0,1)&\\ (0,-1)&\\ (-1,0)&\\ (-1,1)&\\ (-1,-1)& \end{array}\)
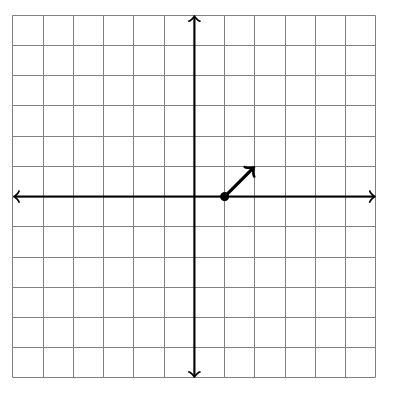
- Repeat the above for the vector field $\vec F(x,y)=(-2y,3x)$, constructing a vector field plot consisting of 8 vectors.
Task 4.4
The last problem for prep each day will point to relevant problems from OpenStax. Spend 30 minutes working on problems from the sections below.
- section 3.2: checkpoint 3.7, exercises 75-92
- Arc Length Practice: section 3.3: checkpoint 3.9, exercises 102-112
