Task 26.1
In this task we'll be focusing on locating the average, mean, center, etc., of something.
- Suppose a class takes a test and there are three scores of 70, five scores of 85, one score of 90, and two scores of 95. We will calculate the average class score, $\bar s$, four different ways to emphasize four ways of thinking about the averages. We are emphasizing the pattern of the calculations in this problem, rather than the final answer, so it is important to write out each calculation completely, without doing any simplifying, before calculating the number $\bar s$.
- Compute the average by adding 11 numbers together and dividing by the number of scores ($\bar s=\frac{\sum \text{values}}{\text{number of values}}$). Write down the whole computation before doing any arithmetic.
- Compute the numerator of the fraction in the previous part by multiplying each score by how many times it occurs, rather than adding it in the sum that many times ($\bar s=\frac{\sum (\text{value}\cdot\text{weight})}{\sum \text{weight}}$). Again, write down the calculation for $\bar s$ before doing any arithmetic.
- Compute $\bar s$ by splitting up the fraction in the previous part into the sum of four numbers ($\bar s=\sum (\text{value}\cdot\text{(\% of stuff)})$). This is called a weighted average because we are multiplying each score value by a weight.
- Another way of thinking about the average $\bar s$ is that $\bar s$ is the number so that if all 11 scores were the same value $\bar s$, you'd have the same sum of scores ($\text{ (number of values) }\bar s = \sum \text{values}$ or $(\sum \text{weight})\bar s = \sum (\text{value}\cdot\text{weight})$). Write this way of thinking about these computations by taking the formulas for $\bar s$ in the first two parts and multiplying both sides by the denominator.
We now generalize the above ways of thinking about averages from a discrete situation to a continuous situation. We did this in first-semester calculus when we computed the average value of $f$ using integrals.
- Suppose the price of a stock is \$10 for two days. Then the price of the stock jumps to \$20 for three days. Our goal is to determine the average price of the stock over the total 5 day period.
- Why is the average stock price not \$15? Use any of the methods from the previous problem to show that the average price is $\bar f=\$16$.
- The function $f(t) = \begin{cases}10 &0\leq t<2\\20&2\leq t\leq 5\end{cases}$ models the price of the stock for the 5-day period. The graph below shows both the function $f$ and the average stock price $\bar f$. Show that the area under $f$ for $0\leq t\leq 5$ is 80. Then show that the area under $\bar f$ for $0\leq t\leq 5$ is also 80.
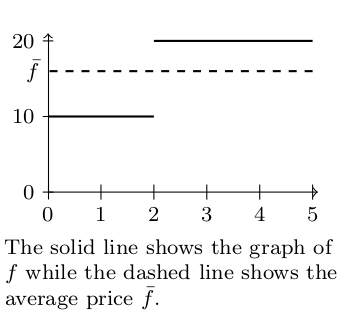
- The average value of a function over an interval $ [a,b] $ is a constant value $\bar f$ so that the areas under both $f$ and $\bar f$ are equal, which means $\ds\int_a^b \bar f dx = \int_a^b f dx.$ Solve for $\bar f$ to show that $$\bar f = \dfrac{\ds\int_a^b f dx}{\ds\int_a^b dx}.$$
Let's examine one last averaging question, this time as it relates to a rover. If we know the mass and center-of-mass of each part of the rover, we can use weighted averages to combine these values and obtain the center-of-mass of the the entire rover.
- Consider a simplified rover with a bottom and a top.
- The bottom part of the rover has a volume of $V_1$ m$^3$, a constant density (mass per volume) of $\delta_1$ g/m$^3$, and a center-of-mass located at $(\bar x_1,\bar y_1,\bar z_1)$.
- The top part of the rover has a volume of $V_2$ m$^3$, a constant density (mass per volume) of $\delta_2$ g/m$^3$, and a center-of-mass located at $(\bar x_2,\bar y_2,\bar z_2)$.
- Give the masses $m_1$ and $m_2$ of the bottom and top of the rover. Explain.
- What proportion of the total mass comes from the bottom of the rover?
- Explain why the center-of-mass of the entire rover is $$\left(\frac{\bar x_1(m_1)+\bar x_2(m_2)}{m_1+m_2},\frac{\bar y_1(m_1)+\bar y_2(m_2)}{m_1+m_2}, \frac{\bar z_1(m_1)+\bar z_2(m_2)}{m_1+m_2}\right) .$$
- The rover picks up an additional object. The object's mass is $m_3$ with center-of-mass $(\bar x_3, \bar y_3, \bar z_3)$. Modify the formula above to give the center-of-mass of the rover, together with the new object. Try writing the formula using summation notation.
Task 26.2
To find the mass of a thin metal plate occupying a region $R$ in the $xy$-plane, we add up the little masses (differentials) $dm = \delta(x,y)dA$, where $\delta$ is the density (mass per area), to obtain the mass as $$m=\iint_R\delta(x,y)dA = \iint_R\delta(x,y) dxdy= \iint_R\delta(x,y) dydx. $$ Note that if $\delta(x,y)=1$, then this reduces to the formula for the area of $R$. This task has you practice setting up area and mass integrals.
For each region $R$ below, draw the region. Then set up an iterated double integral which would give the area of the region. Then use the density provided to set up an iterated double integral that would give the mass of a metal plate occupying this region with the given density. You do not need to compute each integral, rather just set it up.
- The region $R$ is above the line $x+y=1$ and inside the circle $x^2+y^2=1$. The density is $\delta(x,y)=x$.
- The region $R$ is below the line $y=8$, above the curve $y=x^2$, and to the right of the $y$-axis. The density is $\delta(x,y)=xy^2$.
- The region $R$ is bounded by $2x+y=3$, $y=x$, and $x=0$. The density is $\delta(x,y)=7$.
Task 26.3
Consider the change-of-coordinates $x=r\cos \theta$ and $y=r\sin\theta$.
- The lines $r=1,r=2,r=3$ and $\theta=0,\theta=\frac{\pi}{6},\theta=\frac{\pi}{3}$ correspond to circles and lines in the $xy$ plane. Draw these circles and lines in the $xy$-plane.
- The box in the $r\theta$ plane with $2\leq r\leq 3$ and $\frac{\pi}{6}\leq \theta\leq \frac{\pi}{3}$ corresponds to a region in the $xy$ plane. Shade this region in the $xy$ plane.
- Let $(r,\theta)$ be an arbitrary point. Our goal is to develop a formula for the area of the region $R$ in the $xy$ plane where the radius ranges from $r$ to $r+dr$ and the angle ranges from $\theta$ to $\theta +d\theta$, shown in the diagram below.
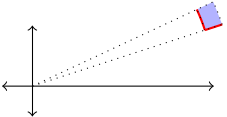
- Add the labels $r$, $\theta$, $dr$, $d\theta$, $r+dr$, and $\theta +d\theta$ to appropriate places in your diagram.
- The shaded region is approximately a rectangle. Letting the width of the rectangle be $dr$, explain why the height of the rectangle can be approximated by $rd\theta$. This means that a little area is give by $dA=rdrd\theta$.
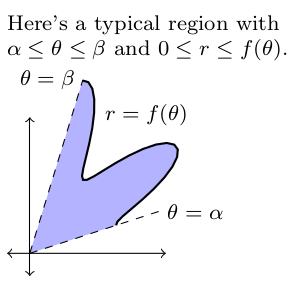
- Consider the region $R$ in the $xy$ plane bounded by $\alpha\leq \theta\leq \beta$ and $0\leq r\leq f(\theta)$ (shown below). The area of such a region $R$ in the $xy$ plane is the double integral $A=\int\int_R dA$. Explain why the area of the region in the $xy$ plane, when using polar coordinates, is $$A=\int_\alpha^\beta\int_0^{f(\theta)} rdrd\theta.$$
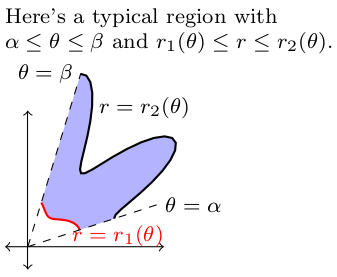
- Now consider the region $R$ bounded by $\alpha\leq \theta\leq \beta$ and $r_1(\theta)\leq r\leq r_2(\theta)$. Set up a double integral that would give the area of this region $R$.
Task 26.4
Pick some problems related to the topics we are discussing from the Text Book Practice page.
